Summary: 2011 sees the introduction of the UltraViolet digital locker platform by DECE, a consortium led by 6 of the 7 top Hollywood studios and backed by 50 more cross-industry heavyweights. This anticipates and supports the transition of film and TV to online distribution. Here we analyse the opportunities telcos will miss out on if they fail to engage with DECE.
Logged-in members can download this 19 page Analyst Note in PDF format. Non-members need to subscribe to read it
Alternatively, please email or call +44 (0) 207 247 5003 for further details. There's also more on DECE UltraViolet strategies at our AMERICAS, EMEA and APAC Executive Brainstorms and Best Practice Live! virtual events.
To share this article easily, please click:In our Executive Briefing entitled, Entertainment 2.0: New Sources of Revenue for Telcos we laid out a series of trends that are changing the video market and the opportunities and challenges this poses for telcos. In this Analyst Note, we examine the ways in which DECE’s UltraViolet will impact the market and explain why telcos can’t afford to adopt a ‘wait, see and proctect approach to its introduction.
DECE UltraViolet has been created in anticipation and support of the switch-over of video content from physical to online distribution. It aims to offer consumers an ultimate level of flexibility as they can not only own, store and manage their content through a digital locker but also share it with family members and view it anywhere through a wide range of devices from TVs and PCs to tablets and mobile phones.
Figure 1 - The UltraViolet proposition: buy once, play everywhere, forever, for the whole family

Source: Telco 2.0
Furthermore, it provides the video industry with a real alternative to piracy based on an open platform with licensable specifications, not a proprietary system such as Apple’s. The platform is set up to support multiple business models and rentals are expected to follow relatively quickly, which explains the interest of Netflix and LoveFilm (now part of Amazon) in the initiative, but at launch it will offer only online purchase.
Finally, the digital locker meta-data will provide a single view of customer buying and viewing preferences on which future planning can be based.
It is not surprising therefore that the initiative has attracted a powerful and active membership comprising in excess of 50 companies including 6 of the 7 major studios, network equipment and consumer electronics vendors, service providers and retailers. Notable exceptions to the current membership are Disney, which has its own digital locker, and WalMart, which has a deal with Apple. Both, however, are free to join at a later date as it is an open platform.
UltraViolet is due to launch in the US in the middle of 2011, with Canada and the UK following towards the end of the year before a full international rollout begins in 2012.
Virtually all the players involved in the video distribution ecosystem from content owners to retailers have their own plays in online video distribution but they are still heavily involved in DECE because they understand that it has the potential to impact on their existing and future business plans. This is not the case with telcos, with a few notable exceptions such as BT which is a member of DECE.
Most telcos seem to be cautious and sceptical about UltraViolet and digital content lockers in general. Rightly or wrongly, they perceive that UltraViolet faces major challenges and represents a headache for them rather than an opportunity.
They appear to doubt that they need digital locker content to drive use of their services and see little margin in retailing movies. Furthermore, mobile network operators in particular are concerned about the impact of video streaming on network congestion and will not hesitate to institute network policy rules that will curtail this perceived “damage”.
Without a clear opportunity for “delivery” income for telcos (for x-plan MBs, QoS, guaranteed bandwidth), or clear business models for moving to this, there is limited incentive for them to step up their interest. We have therefore observed three general telco responses to DECE. For clarity, we have described these as three discreet positions but, in reality, telcos can and do pursue combinations of these.
Telco2.0 believes that there is a potential opportunity for telcos to adopt a more pro-active approach to DECE through an early-adopter strategy as:
Each of these reasons is discussed in detail in the sections that follow.
The global entertainment market is huge and as such is obviously attractive to telcos looking to counter falling ARPUs. It accounts for a considerable share of disposable income and overall entertainment spending is much higher than that on telecoms.
In the UK, which as the leading western European market is to a degree indicative of most developed markets, the average household monthly spend on entertainment is more than double that for communications. Furthermore, the decline in communications spend has been faster than that for entertainment over the last five years and this is despite the rapid decline in music sales revenues.
Figure 2 - Comparative monthly spend on telecoms and entertainment in the UK
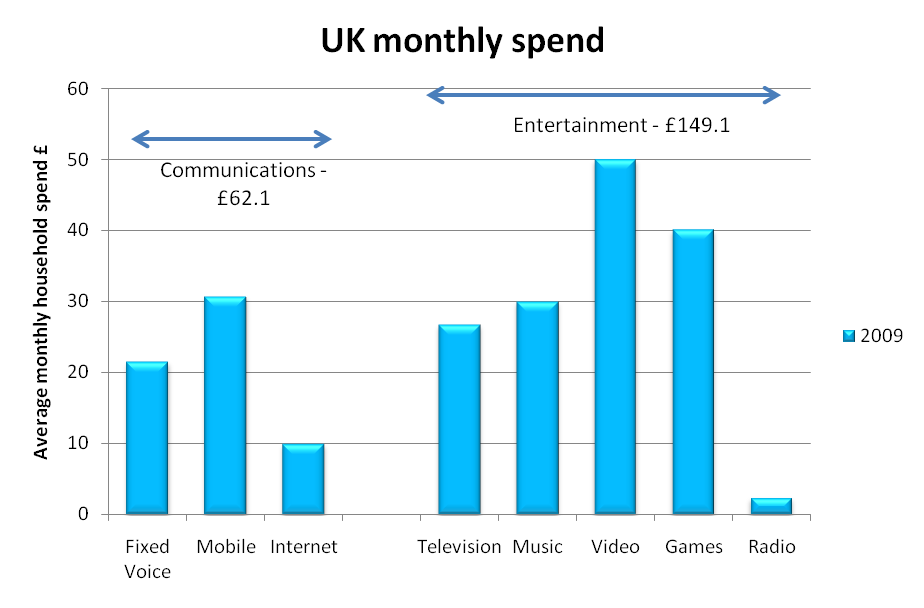
Source: STL Partners Estimates, OFCOM – UK Regulator
Of course UltraViolet is not yet targeting entertainment in its entirety or even all of the home entertainment video market. Instead it is initially setting its sights on the retail market through online sell-through and that is currently very small, accounting for a mere $590 million in 2009 and the lowest contributor of all entertainment sectors to online revenues.
Figure 3 - Digital film downloads are so far the lowest revenue generators in online entertainment
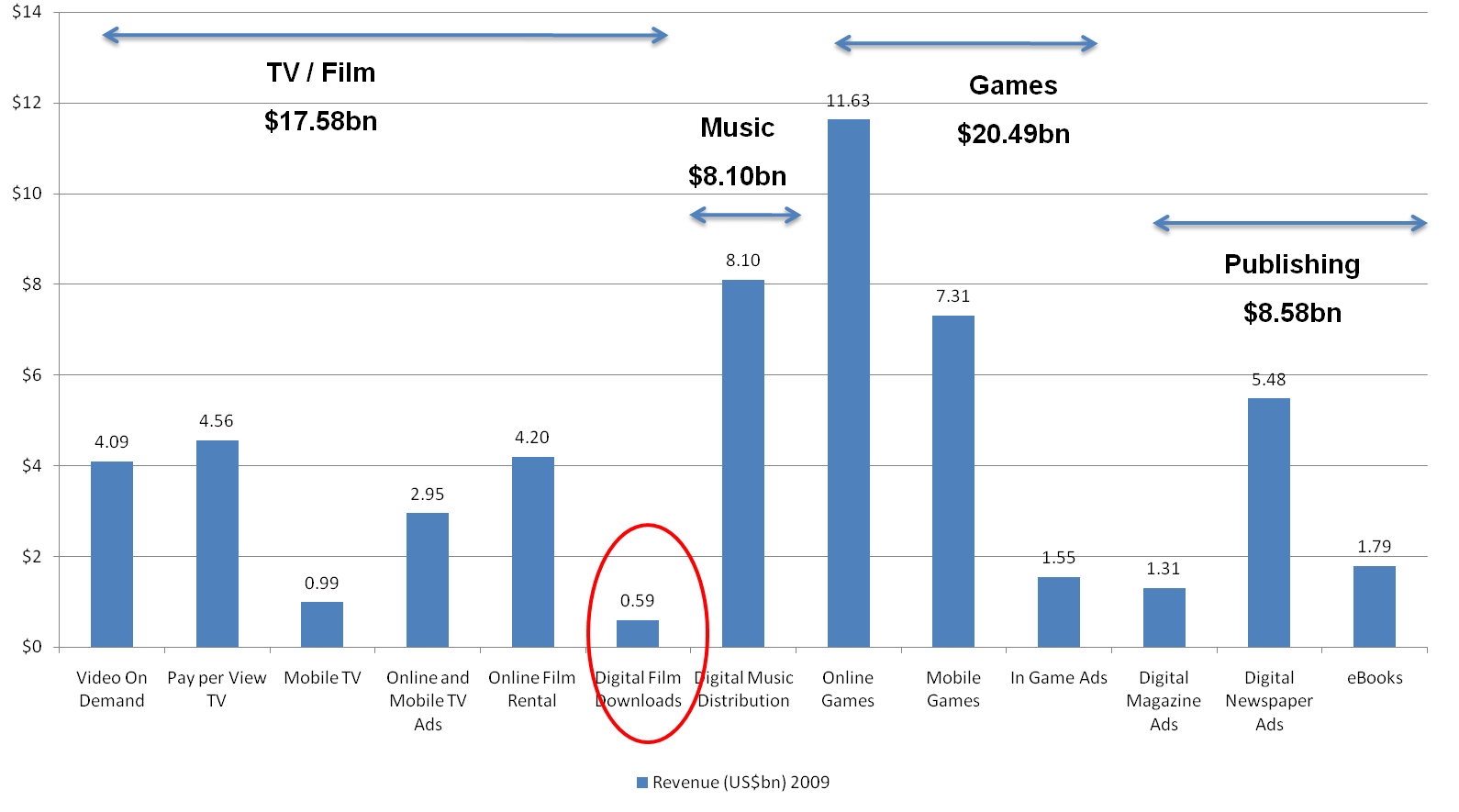
Source: Telco 2.0
It is perhaps not surprising therefore, that telcos have not seen this as a particularly inspiring target segment. However, online sell-through is a nascent market and one we believe has exponential growth potential.
This is certainly proving the case for online rentals. According to Bain’s figures presented at the 9th Telco 2.0 Executive Brainstorm in Santa Monica, 80% of US consumers already view video online and Netflix streaming services now account for 20% of total US internet traffic, twice YouTube’s share. Furthermore, by 2014, 60% of TVs will be connected to the Internet, addressing the major remaining barrier to take up by connecting the primary viewing device to online video content.
Attempts to accurately size future markets are always fraught with inaccuracy, and none more so than punts on film and TV entertainment, as the outcome will always be dependent on the quality and appeal of the content as well as many other factors.
That aside, we are convinced that the market can grow much faster than currently predicted. In fact, we see DECE UltraViolet as capable of stimulating market growth for digital sell-through similar to that of Apple (depicted below). We expect it to grow its share of the home entertainment market from 1% to 13.5%, providing a sizable target market and one that will continue to grow for some time.
Figure 4 - An Apple-style growth is possible for online sell through with UltraViolet
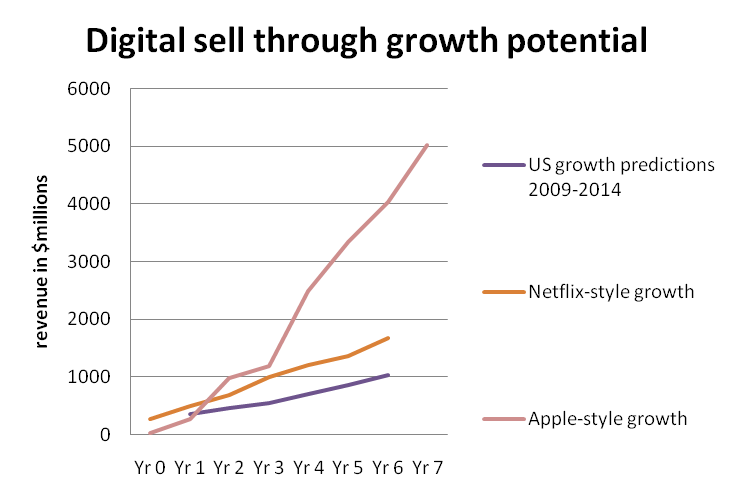
Source: PriceWaterhouseCoopers, Apple, Netflix, Telco 2.0
UltraViolet’s growth potential should at least put it on telco’s ‘strategic interest radar’, especially as it has been designed to accommodate multiple business models, including the rental models in the future.
However, we would argue that waiting for the growth to happen is missing more than one opportunity. The first is to influence in the platform’s development and, perhaps even more importantly, the second is to fit it into and around other strategies that are currently developing in silos, namely video services, customer retention and digital shopping malls.
There is a set of telcos that believe that TV and film content neither offers the kind of margins they require, nor differentiation, as content owners have proven that they are unwilling to negotiate exclusive deals with telcos that can usually only reach a minority proportion of any national market.
Again, we believe this is missing a point for any telco looking to develop a significant retail play. Certainly it is true that margins are low. Tesco, the world’s third largest retailer by revenue, has revealed that it is currently making next to no margin on its physical video business and there is no reason to assume it will be significantly better online. However, the business case for entertainment products developed by what we consider a ‘master retailer' is not based on sales but instead on footfall and the overall size of the shopping basket. Indeed, it is going all out to develop the same relationship online between entertainment product sales and fuller baskets.
Tesco is developing a digital Locker platform that works across multiple devices to deliver a joined up experience and drive impulse buying. It is a staunch supporter of DECE/Ultraviolet and plans on using it, rebranded as InvisiDisc, as a central part of its entertainment platform.
Figure 5 - Tesco puts digital locker at heart of portal proposition

Source: Tesco Presentation, 11th Telco 2.0 Brainstorm, EMEA
As the Tesco example proves, while margins on the products themselves can be small or non-existant, there may be significant other benefits. Tesco see that the overall basket spend is significantly higher when it involves an entertainment product, and entertainment is a both an impulse buy and an attention draw.
Furthermore, the investments that have been made in infrastructure by the DECE group means the entry costs are lower. For the few telcos that don’t have an entertainment platform, UltraViolet offers an opportunity to join the party and use that infrastructure to access what is expected to be premium content which they can offer to customers through their own retail portals. For the majority that already have their own platforms consideration should be given to adding UntraViolet into the mix for what is lost in duplicating infrastructures could be gained with premium content.
Many upstream services rely on the ability to secure consumer attention and sell this on to third parties in some form. This is the basis of the advertising-based business models, including the one that dominates the Internet. Entertainment is a major tool in attracting and maintaining consumer attention as it has such a high profile in the minds and lives of consumers (as exemplified by the UK figures in the chart below).
Figure 6 - Comparative daily usage of entertainment and telecoms in the UK (2009)
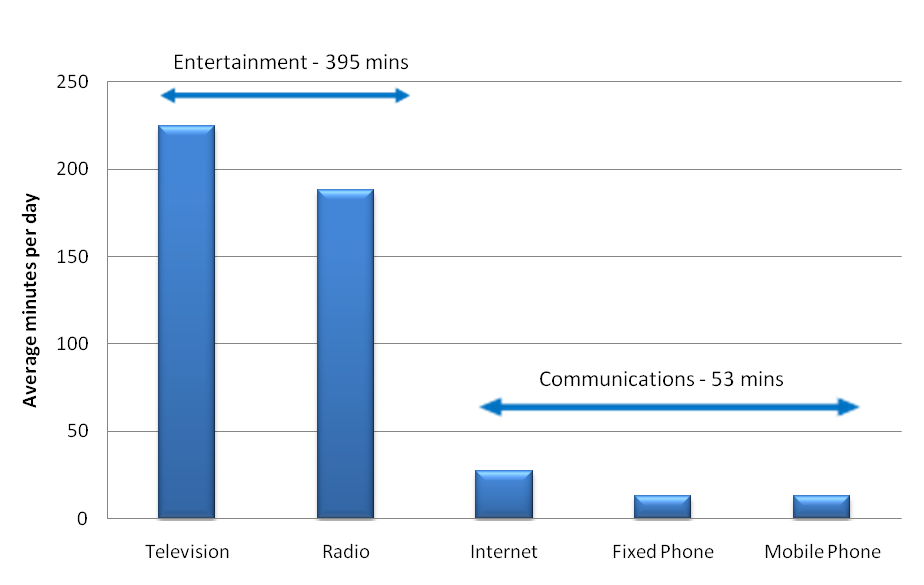
Source: STL Partners Estimates, OFCOM – UK Regulator
The difference in the time spent by consumers on communications services and entertainment is stark and reflects the fact that while communication is a vital part of everyday life, entertainment holds their attention more. This is particularly important and valuable when developing portal and other upstream strategies. as exemplified by the value retailers such as Tesco that are using it as a key part of their online strategy.
The ability of online entertainment delivery platforms to move the needle should not be in question. Netflix and LoveFilm have already made an impact with online rentals, while Apple’s success is indisputable. To do this they have introduced services that have a utility value combined with innovative and disruptive business and pricing models. Using these experiences as a base reference, we have identified the following as important success factors for online distribution platforms:
In theory at least, UltraViolet has strengths across all these.
UltraViolet’s basic proposition of ‘buy once, play everywhere, forever, for the whole family’ is a new and valuable one that overcomes many of the frustrations consumers have with online video content as it offers:
This creates a new and differentiated value proposition and supports the legal transfer of content between people and devices, as well as the capability to view on a full range of devices now and in the future.
It is an open platform based on interoperable standards and licensable technology specifications. So far DECE has laid out some the technical framework for a Common File Format which means video files are encoded and encrypted just once, as well as the technical design specifications for each of the six major categories of company - content providers, retailers, streaming service providers, device and application providers and digital distribution infrastructure providers. These ensure that all players are working in the same way and services will be interoperable. (See Can Telcos Help Save the Video Distribution Industry for more details).
This is a unique and highly valuable proposition and one that has attracted a great deal of support and attention from those currently active in the value chain with the exception of telcos. All the major Hollywood studios bar Disney, which has its own digital locker solution, are behind the initiative which should ensure high quality and desirable content from the start and gives potential access to a huge back catalogue. Indeed, it is widely accepted that the studios will promote new content through UltraViolet first, providing an online alternative to the DVD/Blu-ray sales window.
This is highly significant for telcos that have so far been satisfied to stick to delivering their own content services through VoD, IPTV and mobile believing they have an advantage in providing a multi-screen service as they have the potential to control the delivery quality and have understanding of the user’s device.
However, they are still reliant on content deals with studios to secure the types of films and TV programmes that consumers want. These are usually based around the fourth pay TV window, meaning that consumers would get to new content earlier through UltraViolet than telco VoD services. For this reason we believe that telcos ignoring DECE as part of their downstream consumer entertainment services are missing an important plank in their strategic portfolio.
Furthermore, online service providers are well represented, as are device manufacturers, while traditional retailers, with the notable exception of WalMart which has an existing relationship with Apple, are also putting their weight behind it, providing multiple channels to market.
Beyond the appeal of the consumer proposition, DECE UltraViolet is also appealing because it offers a credible alternative to both piracy and Apple that have dominated the transition of music content distribution online.
As we’ve previously discussed in Digital Hollywood: How to out-Apple Apple, Apple dominates online music and is constantly adding more TV and film content. With over 150 million account holders it is the biggest music retailer in the world and has created the first and so far the dominant business model for digital online retail with its 30/70 revenue share deals. It no longer includes optical drives in any of its current product portfolio as it hopes to drive more film and TV content to its digital store, expanding its content range and reinforcing its existing business model.
To read the Analyst Note in full, including in addition to the above analysis of:
...and additional figures...
...Members of the Telco 2.0TM Executive Briefing Subscription Service can download the full 19 page report in PDF format here. Non-Members, please see here for how to subscribe. Please email [email protected] or call +44 (0) 207 247 5003 for further details. There's also more on DECE UltraViolet strategies at our AMERICAS, EMEA and APAC Executive Brainstorms and Best Practice Live! virtual events.